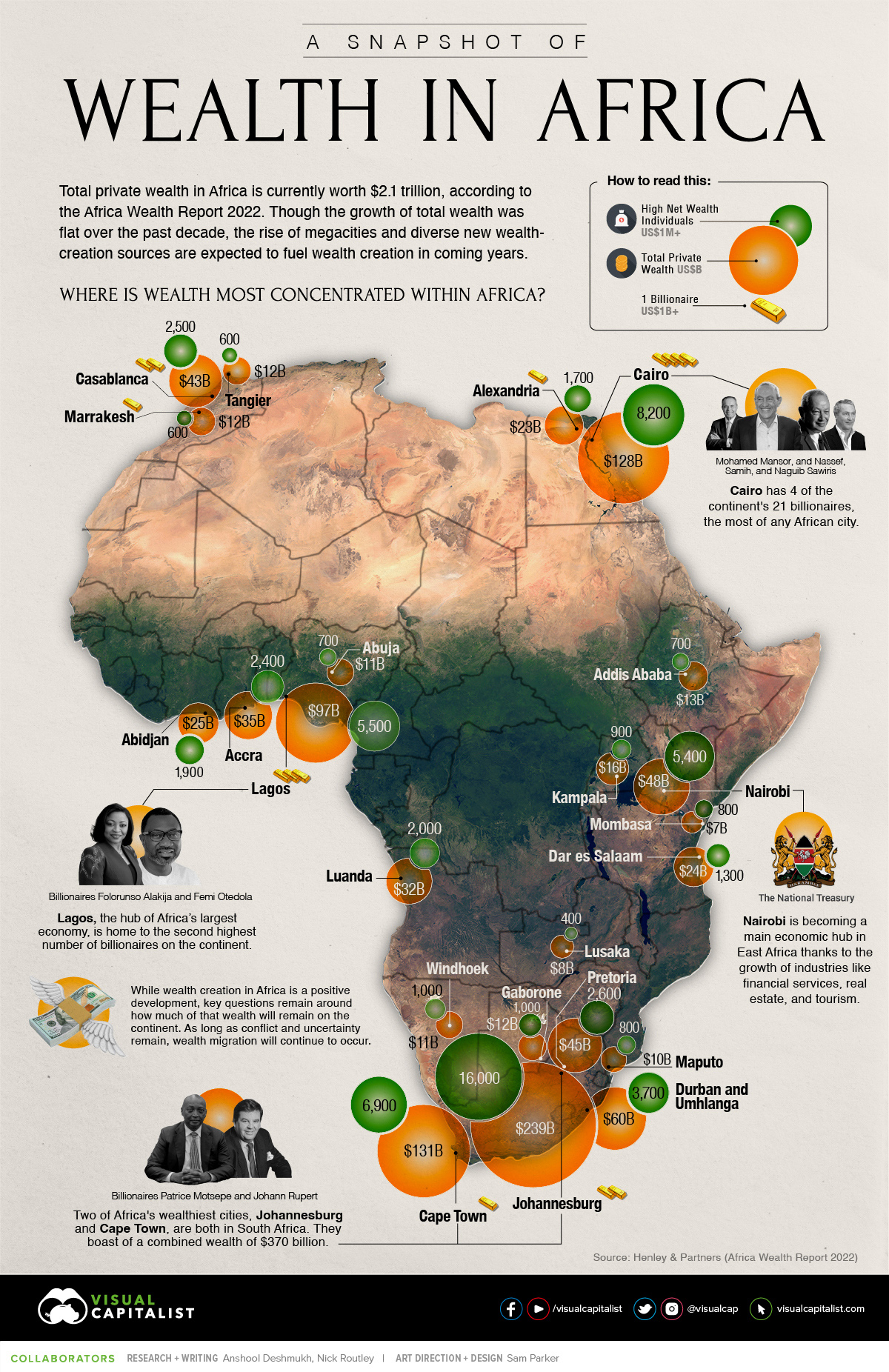
The continent of Africa contains more than 50 countries, but just five account for more than half of total wealth on the continent: South Africa, Egypt, Nigeria, Morocco, and Kenya.
Despite recent setbacks in Africa’s largest economies, wealth creation has been strong in a number of areas, and total private wealth is now estimated to be US$2.1 trillion. There also an estimated 21 billionaires in Africa today.
Drawing from the latest Africa Wealth Report, here’s a look at where all that wealth is concentrated around the continent.
A Country-Level Look at Wealth in Africa
South Africa is a still a major stronghold of wealth in Africa, with a robust luxury real estate market and ample wealth management services. The country is also ranked second on the continent in per capita wealth. That said, the country has faced challenges in recent years.
An estimated 4,500 high net worth individuals (wealth of US$1 million or more) have left South Africa over the past decade, migrating to places like the UK, Australia, and the United States. In one stark data point, the report points out that “there are 15 South African born billionaires in the world, but only 5 of them still live in South Africa.”
Here is how major African countries compare in terms of per capita wealth.
Mauritius is Africa’s wealthiest nation on a per capita basis. Here are a few reasons why the island nation comes out on top:
- HNWI growth – Wealthy individuals have flocked to Mauritius in recent years
- Ease of doing business – Mauritius ranked 13th worldwide in World Bank’s Doing Business Report
- Low taxes – There is no inheritance tax or capital gains tax in the country
- Safety – Mauritius was recently rated by New World Wealth as the safest country in Africa
- Financial sector – A growing local financial services sector and stock market (SEMDEX)
As a result, Mauritius has seen the strongest growth in total private wealth over the past decade, followed by Rwanda and Ethiopia.
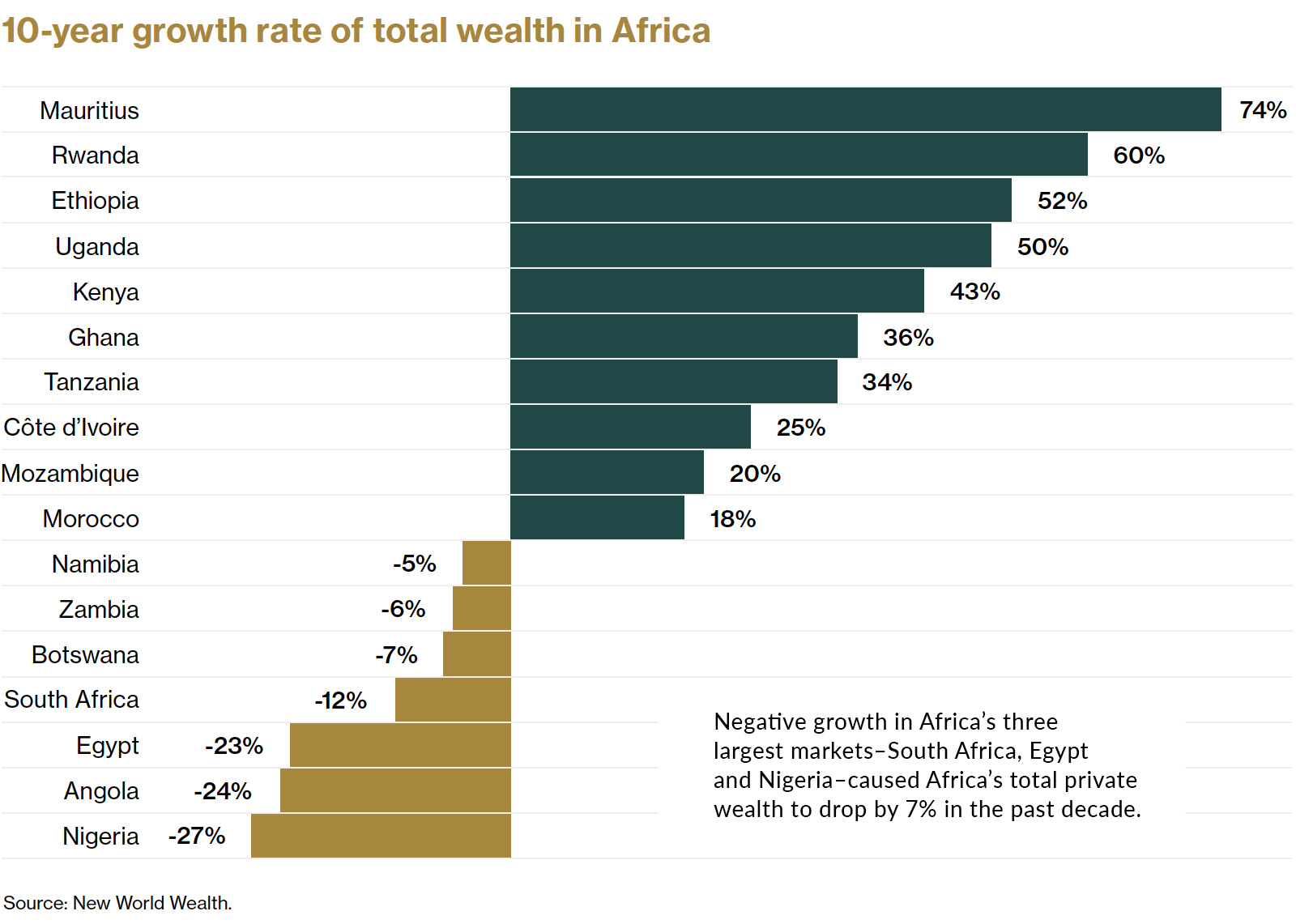
On the flip side of the equation, Nigeria—which is Africa’s largest economy—saw a steep drop in total wealth. The country has struggled in recent years with high unemployment, corruption, and an over-reliance on crude oil.
The Big Picture
Over time, African countries are becoming less dependent on extractive industries, and business conditions are continuing to improve nearly across the board. These tailwinds, combined with the continent’s favorable demographics, point to a bright economic future for Africa.
The outlook for private wealth on the continent is largely positive as well. Total private wealth held in Africa is expected to reach US$3 trillion by 2031, an increase of close to 40%.

Mauritius, island country in the Indian Ocean, located off the eastern coast of Africa.
Physiographically, it is part of the Mascarene Islands.
The capital is Port Louis.
Mauritius lies about 500 miles (800 km) east of Madagascar in the Indian Ocean.
Its outlying territories are Rodrigues Island, situated about 340 miles (550 km) eastward, the Cargados Carajos Shoals, 250 miles (400 km) northeastward, and the Agalega Islands, 580 miles (930 km) northward from the main island.
Mauritius also claims sovereignty over the Chagos Archipelago (including Diego Garcia), some 1,250 miles (2,000 km) to the northeast, although this claim is disputed by Britain.
Relief and drainage
The island of Mauritius is volcanic in origin and is almost entirely surrounded by coral reefs. The northern part is a plain that rises to a central plateau, varying in elevation from about 900 to 2,400 feet (270 to 730 metres) above sea level. The plateau is bordered by small mountains that may have formed the rim of an ancient volcano; the highest point (2,717 feet [828 metres]) is Piton de la Petite Rivière Noire in the southwest. The two major rivers, the Grand River South East and the Black River, are the primary sources of hydroelectric power. Lake Vacoas, one of the main reservoirs, is the chief source of water.
Soils and climate
More than half of the country’s area is arable, and it is almost entirely planted in sugarcane, the major export crop. Vegetables and tea for local consumption are also grown.
Plant and animal life
The vegetation includes some 600 indigenous species, even though little original forest is left. The fauna includes the samber (a long-tailed, dark brown deer), tenrec (a spiny insectivore), and mongoose, as well as a variety of birds and insects. The island was once home to the dodo, a flightless bird that was extinct by 1681. Efforts began in the late 20th century to save several other species of endemic birds that were close to extinction.
People
Ethnic groups, languages, and religion
Approximately two-thirds of the population is of Indo-Pakistani origin, most of whom are descendants of indentured labourers brought to work in the sugar industry during the 19th and early 20th centuries. About one-fourth of the population is Creole (of mixed French and African descent), and there are small numbers of people of Chinese and Franco-Mauritian descent.
Although English is the official language, it is spoken by a very small percentage of the population.
Creole, a French-based patois, is spoken by about four-fifths of the population and is the lingua franca of the country. Bhojpuri, an Indo-Aryan language, is spoken by one-tenth of the population, and French is spoken by a small percentage.
Other languages spoken on the island include Hindi, Chinese, Marathi, Tamil, Telugu, and Urdu.
Mauritians commonly speak two, three, or even more languages, and the educational system supports a wide range of language instruction.








